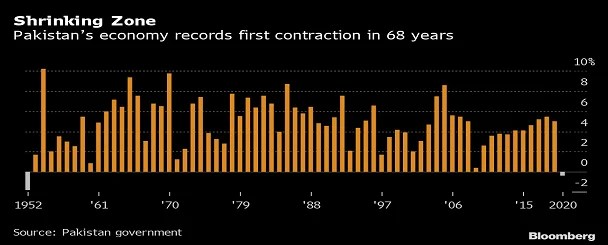
Budget of any country always have huge impact on government itself, private businesses, civil society, and the public in general and specific at the time of ongoing pandemic situation across the country, an important debate has evolved in many circles regarding the degree to which the scourge of coronavirus (Covid-19) might impact the Pakistani economy. If we evaluate our economy’s aggregate expenditure model we can easily understand how vulnerable each might be to a corona contagion at multi-durational intervals of three, six, and 12 months in the initial phases.
The major areas where government focus includes:
- Prioritizing the businesses of E-commerce and digital sector to better utilize the current situation.
- Digitalization transformation of economy by setting priorities:
- Distance & Digital Learning
- Distance Diagnostics
- E-Commerce
- Digital Financial Systems
- Work from Home
But digital transformation has few challenges:
- Digital technologies are highly interdependent and constitute a dynamic ecosystem which includes: communication infrastructure, digital platforms, digital economy skills, local ICT services and content industries, service transformation for all sectors, cyber policies, and ICT sector leadership and regulatory institutions. Maximizing digital dividends requires nurturing this digital ecosystem and tapping into its synergies at the national, local, and sector levels.
- Leadership and institutional capabilities the ICT sector to plan and implement digital transformation strategies. These capabilities are increasingly important to engender shared vision, mobilize long-term commitment, integrate ICT opportunities and investments into development strategies, align complementary policies concerning competition and skills, and pursue partnerships with civil society and the private sector.
- Digital transformation demands substantial investment in organizational capabilities by process innovation, and institutional learning. Best practice suggests that every dollar invested in ICT should be matched with a $4 or $5 investment in process improvement, training, change management, etc.
- Developing nations have the chance to gain from the experience of front runner nations while structuring and formulating policies that address their own issues and fit the local needs by transforming the retailers into e-tailers and it is also the responsibility of state to provide digital framework for Businesses.
Government is trying its best to target these issues by setting priority given in the budget to resolve the issues.
- Health system must be given priority.
- Regional public health institutions are facilitated to exchange information and lessons among countries, link fragmented efforts by multiple stakeholders, develop region- wide policies and interventions, and provide guidance on resource allocation decisions.
- The areas which lacks internet facilities public private partnerships is used (Telco’s) hotspot system must be installed like India to facilitate distance learning system and Government just formulate and ensures policy implementation.
- Instead of attracting foreign tourism government first try to ignite domestic tourism along with Sops.
- To ensure the effectiveness of special package announced by SBP for SMEs reduction in compliance are required especially for the SMEs involved in exports.
- FBR documentations in special credit schemes must be reduced.
- Through supporting SMEs government will create jobs that accommodate expatriate unemployment.
- Government is striving hard to identify the industries which are excluded to access to facilities announced by government by finding the gaps.
- Instead of announcement of risk sharing facility by ministry of finance commercial banks are reluctant to provide loans to SMEs due to the high risk in feasibility and indefinite time to retain their cash flows so, government is working to build the confidence between ministry, SBP and Commercial banks.
- Government announce to reduce direct taxation including corporate taxes to be in line with other countries to minimize current and future burdens on SMEs as most of developing countries who offer less than 30%.
- Government remove excise duties on many products to boost trade.
- Government ensure the availability of announced facilities to all SMEs as banks are reluctant so, Government is trying to attach these credit facilities with FBR as electronic data of all industries are available at FBR and after reviewing the tax profile of industry loans are allocated.
- Tax harmonized schemes are announced because after eighteenth amendment where all provinces have their own tax collection units other than FBR, SMEs are required to submit their taxes at 13 different platforms which will increase the transaction cost for SMEs. Government is trying to reduce the platforms by setting one window operation.
- Instead of operating separate units of tax collections; uniform tax base and tax rates are recommended to implement in all provinces in the budget.
- Instead of announcing general subsidy targeted subsidies are announced for MSMEs instead of providing benefit to SMEs and also ensured to promote innovation and entrepreneurship within the organizations to promote local solutions to build the eligibility to support innovation culture.
- Other than the tax several regulations/compliance on environment, labor and municipal level are enforced on SMEs so Government announce to evaluate Risk Impact Assessments which is conducted in 2005 In order to rationalize the RIA to reduce the compliance (almost 126 licenses levies, permits etc are required in an year) to come out with Covid-19 crisis. Every province is required to review their RIA.
- Govt. announce subsidies to the imported machineries of the cold storage in budget.
- Government fixed the prices of wheat similarly, government announce to fix the prices for other basic food so that farmers receive the direct benefit by removing the role of middle man or moderator through which this extra earning must be transformed into reinvestment in the sector.
- Furthermore, there has been sustained pressure by steel manufacturers to reduce turnover tax on their dealers, inadvertently opening up a new revenue stream for the government as turnover taxation discourages dealers from entering the tax net.
- Non-tax revenues will also remain in focus. Petroleum levy, an important component of the non-tax revenues, is likely to remain low as the government is practicing the policy of not completely passing on the impact of higher international petroleum products prices to end-consumers by taking a hit on petroleum levy.
- The government may adopt a more targeted approach towards power subsidy, which in last year’s budget amounted to Rs140bn. However, the government is expected to keep total subsidies at around Rs530bn compared to last year’s budget of Rs209bn.
- All these expected measures together are likely to keep pressure on fiscal balance. Maintaining fiscal stability and improving fiscal health while adopting a pro-growth and expansionary fiscal policy will be a real challenge for the government. Successfully striking this balance depends largely on successful negotiations with the IMF. The actual budget is not expected to be significantly different from the commitments made to the IMF earlier; however, IMF may allow some relaxation in tax collection targets, albeit setting them close to Rs6 trillion. It is pertinent to mention that Pakistani authorities are presently in talks with the IMF for the finalization of the proposed budgetary measures. There remains a possibility that some of the above measures do not appear in the final announcement, in the interest of keeping the fiscal deficit low.
[box type=”note” align=”” class=”” width=””]The contributor is MD Innovation Summit by IRP/ Bahria University Karachi[/box]



